For enterprises, investing in Internet of Things (IoT) deployments is more than leveraging today’s technology—it’s about preparing for the future of connectivity. With 5G now widely deployed, the next evolution in wireless technology is generating buzz: 6G. Many business leaders and technologists are asking, “When is 6G coming, and how will it impact 5G and 4G LTE?”
Each mobile network generation generally follows a 10-year cycle, bringing new capabilities and features. However, the arrival of the next generation doesn’t render its predecessor obsolete immediately. Understanding the timeline for 6G and its potential impact is essential for planning enterprise connectivity strategies.
Read More: The Quantum Computing Revolution: Pioneering a Bold, Transformative, and Game-Changing Era in 2025
6G: Timeline and Roadmap
6G is expected to launch commercially by 2030. Research and initial requirements gathering are already underway, following the pattern of previous network generations. Standardization and specification development are scheduled between 2025 and 2029, with lab testing and pilot programs beginning in 2028, paving the way for full commercial release.

Subsequent releases, including 3GPP Release 19, will lay the foundation for 6G, with further refinements expected through Releases 20–22. Historical release patterns suggest a development cycle of 2–2.5 years per release, supporting the anticipated 2030 launch for commercial 6G networks.
How 6G Differs from 5G

While 5G has already transformed IoT and mobile connectivity, 6G promises even greater advancements. The primary technological difference lies in frequency: 6G will leverage higher bands, potentially above 100 GHz and possibly approaching 1 THz, providing faster speeds, lower latency, and higher capacity. These improvements will unlock entirely new use cases beyond what 5G currently supports.
Key Advantages of 6G Over 5G
Experts anticipate several major benefits of 6G for enterprise and industrial applications:
- Higher capacity: Utilizing sub-THz spectrum from 30 to 300 GHz.
- Enhanced coverage and reliability: Targeting 99.99999% uptime.
- Ultra-fast speeds: Potentially up to 1 terabit per second.
- Reduced latency: Supporting microsecond-level responsiveness.
- Improved spectral efficiency: Up to three times greater than 5G, reaching 100 bps/Hz.
- Expanded mobility support: Effective at speeds up to 1,000 km/h (600 mph).
Challenges Facing 6G
Despite its promise, 6G faces significant hurdles:
- High-frequency communication: Bands above 100 GHz require new radiofrequency designs and advanced semiconductor materials.
- Processing speed: Achieving terabit-per-second rates may demand optical or quantum computing solutions.
- Energy consumption: While 5G is already 90% more energy-efficient than 4G, denser 6G networks could drive power demands even higher.
Potential Use Cases for 6G
6G is expected to enable transformative applications:
- Full-sensory digital and augmented reality experiences.
- AI integration at the network edge for real-time analytics.
- Industrial IoT for smart factories and automated production.
- Tactile Internet for transmitting touch and haptic sensations.
- Autonomous vehicle operations with ultra-low latency.
- Advanced virtual healthcare solutions.
Will 6G Replace 5G or 4G LTE?
The transition from one mobile generation to the next often includes overlapping usage periods. For example, 2G and 3G networks remained operational during 4G LTE rollout and some were supported even as 5G emerged.

5G Longevity: The 5G lifecycle will likely extend well beyond 6G’s debut, potentially until 2040. However, technological advances or delays could shift this timeline.
Current Status of 6G
While 6G remains in the research phase, there are promising milestones. For example, a lab in China achieved speeds of 206.25 Gbps under controlled conditions, demonstrating the potential of terahertz connectivity, though commercial deployment is still years away.
6G Devices and Availability
Consumer and enterprise devices typically launch in tandem with network rollouts. Expect first-generation 6G devices around 2029–2031, with broader adoption following nationwide availability. Early devices are often expensive and feature-limited; enterprises typically wait for second-generation products for more cost-effective solutions.
The initial 6G rollout will likely mirror 5G’s early adoption patterns, starting in technologically advanced countries such as the US, China, and South Korea. Global availability may take years, similar to 5G’s gradual worldwide expansion.
Preparing for 6G: The Enterprise Perspective
Enterprises looking to maintain competitive advantage in IoT, industrial automation, and advanced mobile applications should plan strategically for 6G. Key considerations include:
- Assessing current 5G deployment and ROI.
- Monitoring 6G research and pilot programs to anticipate capabilities.
- Planning device procurement and phased network adoption.
- Evaluating vendor solutions with long product lifecycles and integrated management tools.
Digi: Your Partner in Cellular Connectivity
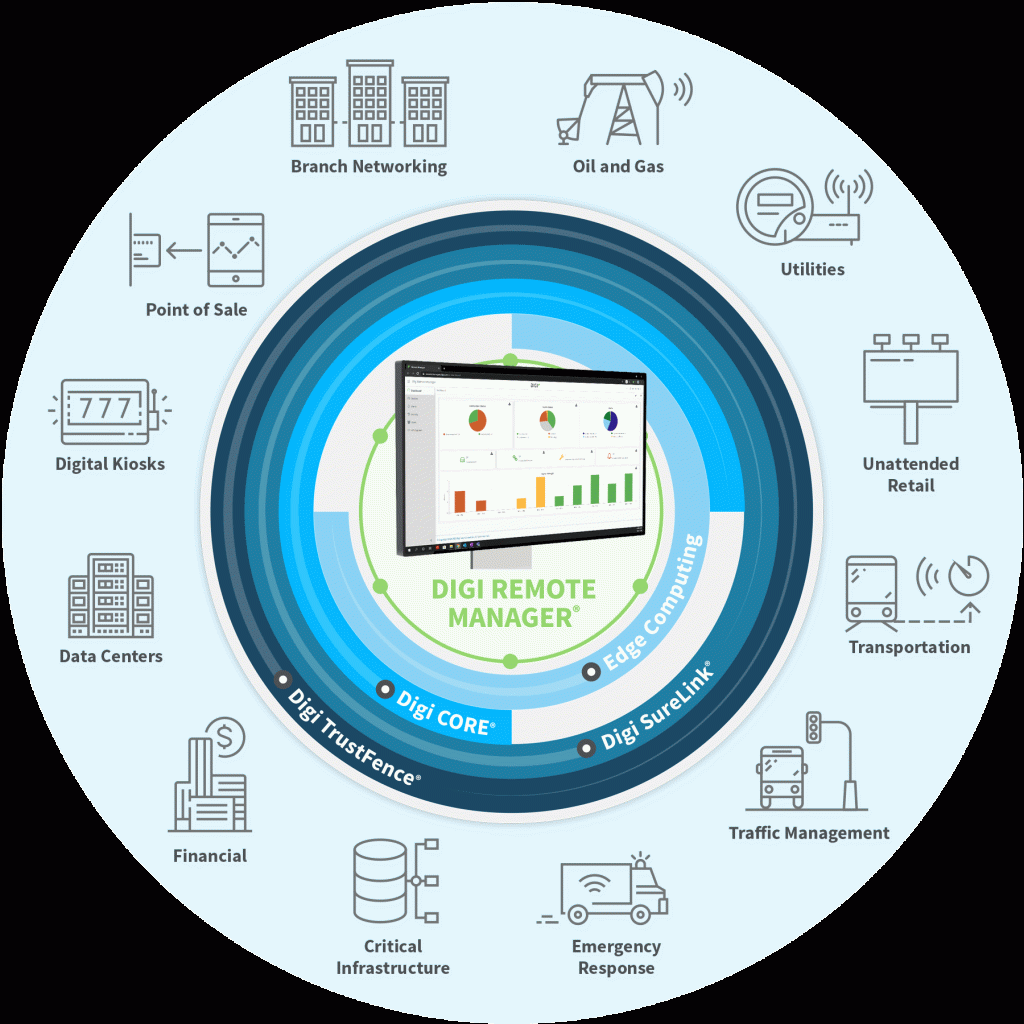
Digi International has been at the forefront of cellular solutions for over two decades, pioneering innovations since the 2G era. Digi provides secure, high-performance IoT and cellular connectivity solutions for enterprises, industrial operations, and transportation networks.
Digi’s end-to-end offerings include industry-leading devices, integrated management platforms, and professional services for planning, deployment, and monitoring. Enterprises can rely on Digi to design scalable, future-ready solutions that meet current needs while seamlessly supporting next-generation connectivity like 5G Advanced and 6G.
By partnering with Digi, organizations can confidently navigate evolving wireless technologies, ensuring reliable connectivity, operational efficiency, and long-term ROI.
Frequently Asked Questions:
What is 6G?
6G, or the sixth generation of wireless technology, is the anticipated successor to 5G. While 5G has revolutionized connectivity with enhanced speeds and lower latency, 6G aims to push these boundaries even further. It envisions ultra-fast data rates, seamless connectivity, and the integration of advanced technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and holographic communications.
Wikipedia
When is 6G expected to launch?
The commercial rollout of 6G is projected for the early 2030s, with some experts estimating a launch around 2030. However, this timeline is subject to advancements in research, standardization processes, and infrastructure development.
Will 6G replace 5G and 4G LTE?
While 6G will offer advanced capabilities, it is unlikely to immediately replace existing networks. 4G LTE and 5G will continue to serve as foundational technologies, with 6G complementing them to handle more data-intensive and latency-sensitive applications.
Will 6G be available worldwide?
The global rollout of 6G will depend on regional infrastructure capabilities, regulatory environments, and economic factors. While early adopters may experience 6G services first, widespread global availability is expected to take several years post-launch.
When is 6G expected to launch commercially?
The first commercial 6G networks are anticipated to roll out around 2030. Standardization efforts are underway, with the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) aiming to finalize specifications by 2029, paving the way for deployments shortly thereafter.
How does 6G differ from 5G and 4G LTE?
6G will operate on higher frequency bands, including sub-terahertz (sub-THz) spectrum, enabling faster data rates, lower latency, and more reliable connections compared to 5G and 4G LTE. While 5G offers speeds up to 20 Gbps, 6G is expected to achieve speeds up to 1 terabit per second (Tbps).
Will 6G replace 5G and 4G LTE?
While 6G will introduce new capabilities, it is expected to coexist with 5G and 4G LTE for some time. The transition will depend on regional infrastructure developments and adoption rates. For instance, 4G LTE may remain operational in certain areas even after 6G is deployed
Conclusion
The arrival of 6G represents the next frontier in wireless connectivity, promising unprecedented speeds, ultra-low latency, and transformative capabilities that will redefine industries and everyday life. While 5G and 4G LTE will continue to play a critical role for years to come, 6G is set to unlock new opportunities in IoT, autonomous systems, immersive experiences, and intelligent networks. Enterprises that proactively monitor 6G developments, invest strategically in infrastructure, and plan for future-ready devices will be best positioned to leverage its full potential. As research progresses and global deployments approach, staying informed and adaptable will be key to navigating this technological revolution.